What is the difference between a servo and stepper motor?
Stepper motors are composed of a rotor, stator, permanent magnet, and driving circuit. They rotate by a fixed angle for every input signal, providing high accuracy, low noise, and rapid start and stop.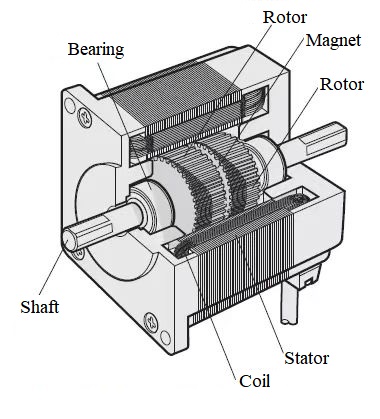
we will compare and analyze stepper motors and servo motors from various aspects in below, including working principles, control precision, speed and overload capacity, operational performance, and cost.
Working principle
There are significant differences in the working principles between these two types of motors. A stepper motor operates using an open-loop control system, receiving electrical pulse signals to rotate and convert them into angular or linear displacement for precise control. The rotational accuracy and speed of the stepper motor are influenced by the step angle and pulse frequency.
On the other hand, a servo motor uses a closed-loop control system to achieve precise position control. The servo motor has the function of emitting pulse signals, A corresponding number of pulses are emitted for every single rotation. The controller receives and processes these pulse signals, and converts the difference between the target position into control signals for the motor.
Torque at lower speed
Stepper motors provide higher torque at low speeds than servo motors, which makes them suitable for many applications that require high torque, such as printing machines, packaging machines, and textile machines. The high torque characteristics of stepper motors also make them suitable for applications that require rapid acceleration and deceleration
Speed range
In terms of rotational speed, stepper motors have a relatively low speed, usually below 1000rpm, while servo motors can achieve higher speeds, typically above 3000rpm. So stepper motors are often used in in low-speed applications, such as in printers, scanners, and surveillance cameras, where precise and slow movements are needed. While servo motors are often used in high-speed applications, such as in industrial automation, robotics, and aerospace systems.
Operation difficulty
Stepper motors are relatively simple to operate and control because they do not require position and speed feedback. The controller only needs to provide pulse signals to the motor to make it rotate, which makes stepper motors easy to use and maintain. In contrast, servo motors require feedback controllers to achieve high-precision and high-speed motion, which makes their control system more complex and requires more parameter adjustments and debugging. Servo motors usually require professional technicians to adjust hundreds of parameters
Control precision
Stepper motors achieve precision control by precise adjustment of the step angle, using various subdivision levels. In comparison, servo motors rely on rotary encoders to ensure control precision, which is typically higher than that of stepper motors. Stepper motors have evolved to become increasingly precise and versatile, with subdivision and encoder technologies enabling their use in 3D printing, CNC machines, and medical devices. Servo motors are the preferred choice for high-precision applications in robotics, aerospace systems, and industrial automation.
Cost
Stepper motors are generally cheaper than servo motors because of their simpler structure and lower production costs. Stepper motors do not require sensor feedback or advanced controllers to achieve high-precision motion, which makes them more cost-effective .Generally servo motor price is dozens times of stepper motor price.
In conclusion, stepper motors and servo motors have their unique advantages and disadvantages. The choice is based on applications. While with the development of technology,it has led to the emergence of a hybrid solution – closed-loop stepper motors, also known as closed-loop step motors or closed-loop stepper drives. These motors combine the precision and speed control of servo motors with the high torque and low cost of stepper motors, making them ideal for applications that require high precision, speed, and torque. The closed-loop step motor uses a feedback loop to ensure accurate position control, making it an attractive option for industries such as robotics, automation, and medical devices.


