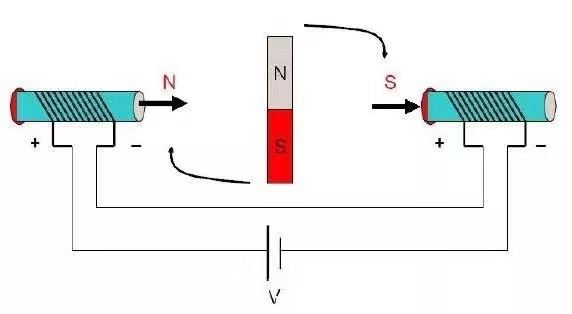
Why are BLDC motors called DC motors while they run on AC?
BLDC, also known as Electronic Commutation Motor (ECM) is a type of synchronous motor that uses a direct current (DC) power supply.
Essentially, the BLDC motor is a permanent magnet synchronous motor that converts a DC power source into a three-phase AC power source. The AC power generates electromagnetic force to drive the motor to rotate. Despite BLDC actually works on AC, why are they called DC motors? We can explain it from its history and working principle.
History of motors
The first DC motor was born in the 1840s. It was a significant milestone in the history of electrical engineering. However, the first DC motor had two main drawbacks: high capital cost and high running maintenance cost that limited its widespread use.
The cost of materials, manufacturing and specialized labor required for its construction made it an expensive technology to produce. Additionally, regular maintenance was necessary to replace the brushes and resurface the commutator, which added to the overall cost of using the motor. Because of the above, it was not affordable or practical for many potential users.
In the 1890s, the AC motor was introduced to the world, quickly gaining popularity for its simple structure, reliable performance, and low cost. This groundbreaking invention represented a significant improvement over its DC counterpart, with several advantages such as easier maintenance, fewer parts, and better insulation.
However, the AC motor also had several drawbacks. One of the significant limitations of the AC motor was its difficulty in self-starting. The low power factor was another issue, resulting in lower overall efficiency compared to DC motors. The speed regulation range was also limited, making it challenging to regulate the speed over a wide range.
So, researchers again went back to DC motor despite having a list of disadvantages. Such as brush wear, noise, and sparks during operation, which limit their application in certain fields. To solve these problems, brushless DC motors were born.
Brushless DC motors were first developed in the late 1960s. Unlike traditional brushed motors, brushless motors no longer have brushes on their rotors. This brushless design eliminates friction and sparks, and allows for more precise control of the motor’s operation. Additionally, brushless motors have higher efficiency and longer lifespan, making them an important development direction in modern motor technology.
Working principle of BLDC motors
BLDC motors consist of a stator winding and a rotating magnetic pole. The magnetic field between them follows the Lorenz theorem, which states that the interaction between current and magnetic field produces force. When the stator winding is energized, it generates a magnetic field around it, which interacts with the magnetic pole of the rotor, causing the motor to rotate. The driver periodically changes the direction of the current in the stator winding to control the stable rotation of the motor. In addition, the driver can also control the speed and position of the motor based on feedback information from sensors.
The driver converts the DC into an AC through electronic devices to control the motor’s direction and speed. The driver can use various methods to convert the DC into an AC, with one commonly used method being PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controllers. The PWM controller produces an output signal similar to a sine wave by periodically adjusting the duty cycle of the power supply voltage, to control the motor’s rotation speed and direction.
AC or BC power input ?
Brushless motors can use both low-voltage DC and high-voltage AC. If the bldc motor controller is connected to AC, the driver converts AC to DC for the motor to work. If DC is input, the brushless motor controller does not need to convert. High-voltage AC power is easy to obtain and can provide motor power.
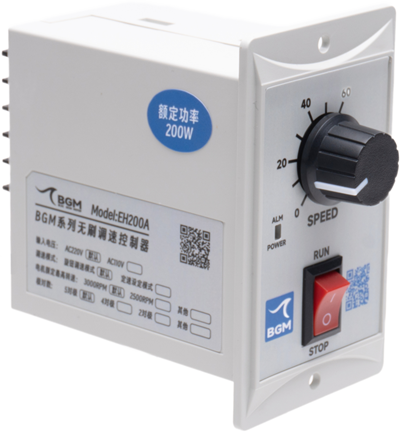
High-voltage AC BLDC motors are suitable for applications that require long-distance energy transport and high performance applications such as industrial robots and automated production lines. BGM company’s EH200A is a newly developed high-performance and low-cost AC brushless speed controller. It is for brushless motors with 200W and lower power. Motor speed can be regulated by the rotary knob of the controller easily. Contact us for more information!
While low voltage BLDCs are preferred for low-cost, high-reliability, and easy-to-maintain applications such as power tools and household appliances. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on factors such as power density, efficiency, control precision, reliability, and cost.
In conclusion, the development of BLDC motors has revolutionized the motor industry by addressing the limitations of traditional DC and AC motors. With their high efficiency, longer lifespan, and precise control, BLDC motors are now widely used in various applications such as electric vehicles, drones, and industrial automation. Despite their name, BLDC motors work on AC, and their ability to use both DC and AC power input adds to their versatility. As motor technology continues to evolve, it will be exciting to see what innovations and applications the future holds for BLDC motors